Today’s Class – Web Security Workshop
- Ensure Basic Website Security
- Research These Terms
- Upload the Complete File on MyKangan
- Internet Security
- Protect Fixed Internet Connection and IP Address
- Use and Maintain Antivirus Software
- Protect Shared Network Resources From Intrusion
- Following Security Protocols
- Disable Control Protocol
- NETBIOS and TCP/IP
- Assessment Task
- Feedback
Ensure Basic Website Security
Today we will have to insert a workshop on basic Website security.
This is the unit of competency that we will cover:
Read the units’ elements:
- Determine Business Security Requirements
- Ensure Web Server Security
- Ensure Protocol Security
Research These Terms
Use this link TechTerms.com, Webopedia.com and find your own web dictionary to research the terms below:
- What is a (Web) Host/(Web) Hosting?
- What does ISP stand for?
- Example of 2 free hosting services (provide links)
- What is FTP?
- What is a Domain name?
- Explain IP Address and give an example!
- What is the difference between a static and a dynamic IP address?
- Find and list prices for a domain name made up of your name on http://who.is/
- What is the difference between a server and a PC?
- What is a Web Server?
- What is a Gateway?
- Give an example for a Gateway.
- What is the purpose of a Firewall and where is it located?
- What is meant by Malware?
- Give 3 examples for Malware!
- How can you protect your computer against Malware?
Give three examples of software designed to protect your computer! - Define HTTP.
- Define HTTPS. How does it differ from HTTP?
- What is a URL?
- Define SSL.
- Explain the acronym TCP! How does it relate to IP?
Upload the Complete File on MyKangan
Create a new Word Document and insert all your definitions in there with the source of your information. Next upload this as a Day 1 Task on MyKangan in ICAWEB408A-Ensure Basic Website Security.
Visual Example of a Network
Visual Example of a Network connected to the Internet: Example of the Internet displayed as networks.
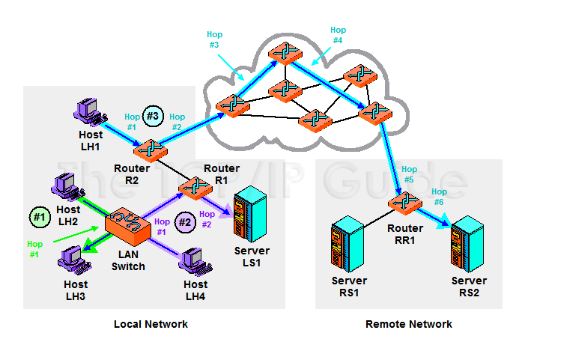
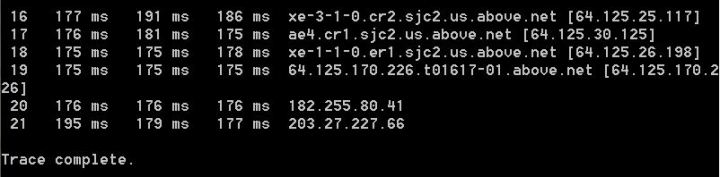
You can view the different routers that your host PC will visit when accessing a Web page:
Launch the command prompt from a Windows-based computer click: Start > All Programs > Accessories
> Command Prompt. Type tracert and hit enter. This process is called tracing route to a website.
Internet Security
I would like to thank Anonymous alias JB for the most of the documentation below.
Read all the information below to be able to complete your assessment task for this unit.
Protect Fixed Internet Connection and IP Address
The IP address is always visible to the outside world. Internally, you can reduce its visibility for non-technical persons but not eliminate knowledge of the address.
- Security updates on server/gateway.
Security exploitation is commonplace today and so it is essential that security patches for gateway machines are kept current.
- Only gateway devices should have public IP addresses, not internal network computers, which should be on a private network address scheme.
Use and Maintain Antivirus Software
It is paramount to not just have Antivirus software installed, but to maintain currency .
Read: Internet Security GCF Learn Free
Protect Shared Network Resources From Intrusion
Sharing is the primary productivity benefit of networking. We have to share resources on the network such as printers and file folders in order to be productive. Some of those resources might be shared outside the local network (eg the incoming mail server) but most local network files and hardware are not meant for use outside the organisation and need to be protected. This may also include computerised machine tools used in manufacture and the building air-conditioning and lighting which may be computer controlled.
TCP/IP is the modern network topology. A key feature of the protocol is that different types of traffic (eg Email, web, telephone) are sent to different ‘ports’. There are 65535 Ports available of which the first 1024 are reserved. Of these 1024 reserved ports, only the first 256 are in common use. That means there are tens of thousands of potential gateways into your network that are not in active use. From a security point of view, these open ports are like open doors to a building, with one important difference. Although they are open, there may not be anything on the other side of the door (an empty room). However, Trojans exploit these ports for communication and open ports are a leading cause of the spread of DDOS and other security threats. The primary function provided by all Firewall services is to control the range of open ports. Only those ports intended to be available for use should be open on the firewall. (Note: KANGAN does not seem to apply this restriction.)
-
Firewall
It is necessary to protect the interface between the local network and the internet by the use of a Firewall. A Firewall will allow management of what links (protocols/ports) are available between the local network and the internet. For example, it would be possible to only allow Email traffic.
A Firewall may either be software running on the gateway or most likely today an Appliance that sits between the Gateway and the Internet. The advantage of an Appliance is that it is purpose built for managing security risks.
-
Password Strength
Weak passwords are the single most common cause of security failure.
Read: Passwords: The First Step to Safety GCF Learn Free
Following Security Protocols
Ensure that personal computer protocols and preferences follow security protocols. (Too many uses of the word protocol here and with different nuances of meaning).
- As the risk of an unexpected new threat is always there, it is essential that there are rules for how information about the internal network is managed. These include, establishing minimum password lengths and types, where business files are saved and how or if visitors are allowed any computer access.
- Ensure that all staff understand security issues and in particular the role of HTTPS in creating secure data links; how to handle suspicious email and what to do if they suspect their computer is infected by a virus or otherwise compromised.
- Ensure that processes exist to install and maintain Antivirus on all workstations.
- Induction program for new staff on computer security and use procedures.
Disable Control Protocol
Disable control protocol or internet protocol bindings for file and printer sharing. (This is not relevant to modern Windows releases which implement security over file and printer access on the TCP/IP network.)
- When a computer is directly connected to the internet, (e.g. at Home) shared printers and shared files are exposed to the internet and this can be exploited, particularly if passwords on the files/printers do not exist or are weak. At home, disabling file and printer sharing would prevent sharing of things such as iTunes on the local network. The better strategy is to make sure you have very strong passwords on the printer and file shares.
- Do not disable or uninstall File and Printer sharing on a Business network. Disabling this will mean that the network cannot operate effectively in sharing data and services, which is its main purpose. In commercial environments (e.g. Kangan), TCP/IP is usually the only network protocol in use and the gateway server/appliance is the first level of defence against outside access. Most modern networks store shared files only on the server with robust security measures controlled by the server software.
NETBIOS and TCP/IP
Ensure that network basic input/output system (NETBIOS) over TCP/IP is disabled.
NETBIOS is a network Applications Programming Interface (API) that was used prior to Windows 2000 / XP to identify the individual computers on the network. Essentially it was the means by which data was directed across the network, by applications, to the computer that required it. It is not really a network protocol as such, more like a utility that software can implement to communicate between machines. It is not secure as it was developed in the context that the network was ‘trusted’ and only local (not internet exposed). NETBIOS is easily exploited to gain unauthorised access.
- NETBIOS exists by default in all Windows releases using TCP/IP, including Windows 8. NETBIOS should not be implemented on any current systems and must be disabled.
- You can disable NETBIOS using Group Policy on the Server or by individually disabling under Control Panel/ Local Network Connections / TCP/IP Advanced Settings / WINS
When Windows 2000 / XP first came out, NETBIOS was required to allow for some applications to work across networks that also had Windows98 machines. Those applications and services that depend on NetBIOS over TCP/IP no longer function once NetBIOS over TCP/IP is disabled.
Assessment Task
Please download the assessment task here (on Wednesday) and upload to MyKangan.
Feedback
Please leave your feedback in form of a comment. Your feedback and suggestions will help me to make this blog more user friendly. Thanks!





































































































![world war propaganda_Auch du sollst beitreten The concept was used on the German side as well with this 'Auch du sollst beitreten zur Reichswehr' [You too should join the German Army], design by Julius Engelhard, Image: courtesy of mental_floss](https://classoffederico.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/world-war-propaganda_auch-du-sollst-beitreten.jpg?w=468&resize=468%2C597#038;h=597)
























